The Idea of modular hardware:
Modular hardware is a concept where a complex circuit is separated into separate modules instead of one complete setup.
In electronics design, it means splitting a complete circuit into multiple smaller PCBs. The PCBs are then connected via cables or connectors.
The concept isn’t new & if you look at how computers are assembled, be it a desktop or your laptop. A single motherboard with slots for graphics cards, sound cards, and other peripherals is what modular hardware is all about.
Reason for modularity:
- Allow reuse, test & upgrade of individual components.
(microcontroller are upgraded every 2-3 years)
- Space Constrained.
- Task-specific customization.

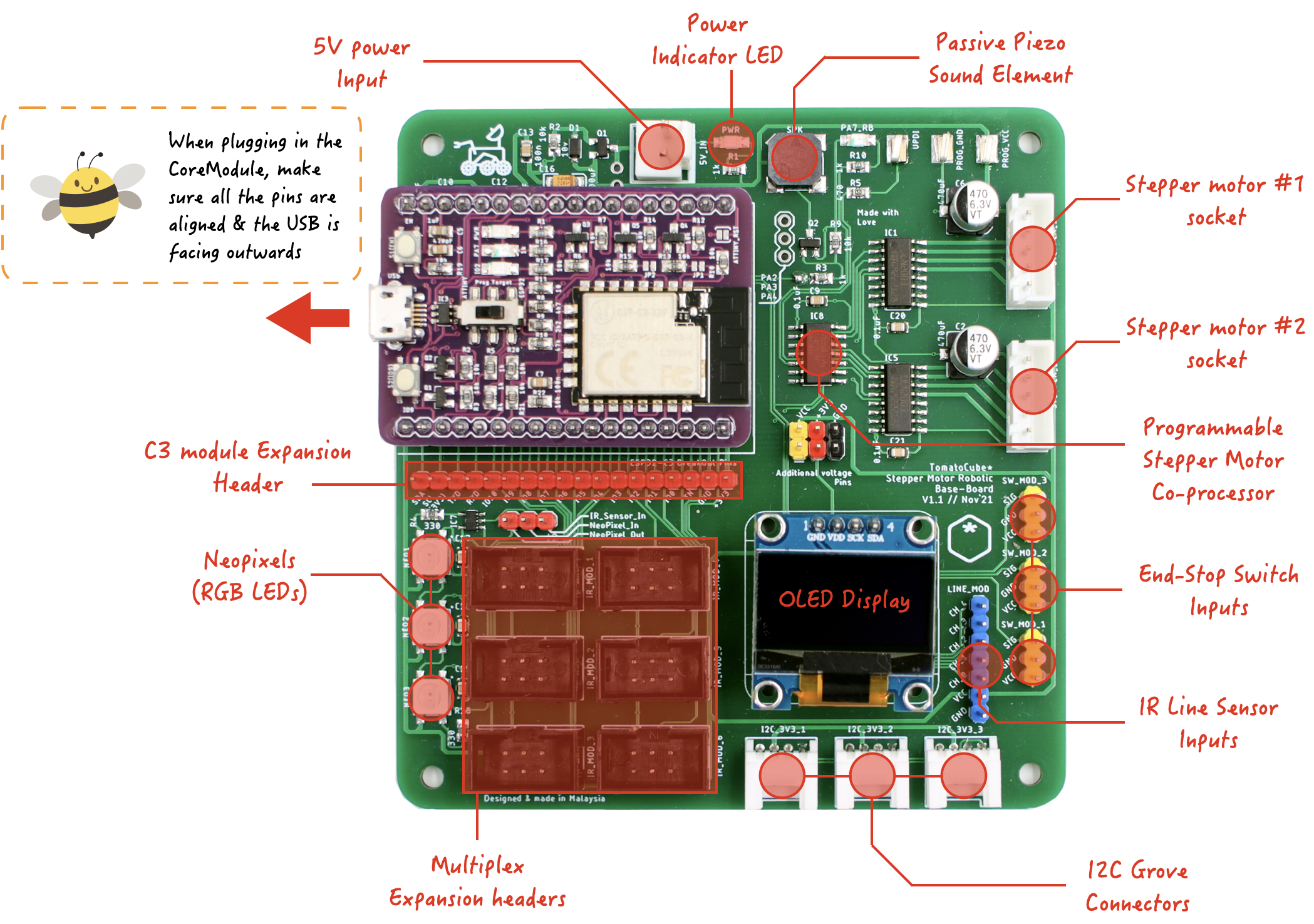
Parts of the Robotic Main Board:
Once the C3 CoreModule is matched up with the Robotic Mainboard, it immediately opens up a world of possibilities.
Here are some of the IO peripheral & modules as well as breakout that is presented on the Robotic MainBoard.
- 1x Sockets for Core module
- 1x Stepper motor co-processor & 2x JST connectors.
- 3x programmable RGB Chain-able Neo-pixels LEDs onboard.
- 1x i2C Graphical OLED display.
- 1x i2C port expanders for various sensors.
- - 3x EndStop (Microswitch) module connection.
- - 1x 5-Channel IR line module connection.
- 3x 3v3 i2C grove connectors for misc sensors/peripherals expansion.
- 1x (unpopulated) 5v i2c grove connectors.
- 6x Shrouded 3x2 pin header for IR modules (or others) expansion.
- 1x Passive Piezo sound element.
- 2x CoreModule Pin header breakout.
- 1x Additional Power Pin header breakout.
The image above shows the location of where the aforementioned breakout pins. Alternatively, you can also observe the printing on the board's silkscreen layer. Again, the printing on the silkscreen layer will give a hint at the purpose of those connections.