In our previous chapters, we have demonstrated how to incorporate Google's Teachable machine into (any) C3 CoreModule projects.
However, our CockroachBot project could also benefit from having a bit more intelligence. What do you say? Can we add the ability so that our CockroachBot can recognize audio cues?
In this experimental workshop, you could even try to make a unique sound to signal a swarm of CockroachBot discreetly to lead a covert mission to take over human civilization.
Think Harriet Tubman's Barred owl call.
Harriet Tubman, an Unsung Naturalist: Owl Calls as a Signal
Harriet Tubman's Secret Owl Signal: YouTube

Creating a Sound Project:
Let's get started by creating an Audio Project in Teachable Machine.
Right away, Teachable Machine gave you two starter classes,
"Background Noise" and "Class 2."
The idea of "Background Noise" is similar to the "Background" class we have in our previous Teachable Machine project. It serves as a control (to detect when no noise is happening at all).
For your audio recognition project to work ideally, make sure to input & collect enough background noise samples for training.
Since I am not as talented as Harriet Tubman, I will just create recognition classes for capturing "Me saying the word GO", "Whistling", "Clapping" & "Snapping of my own fingers".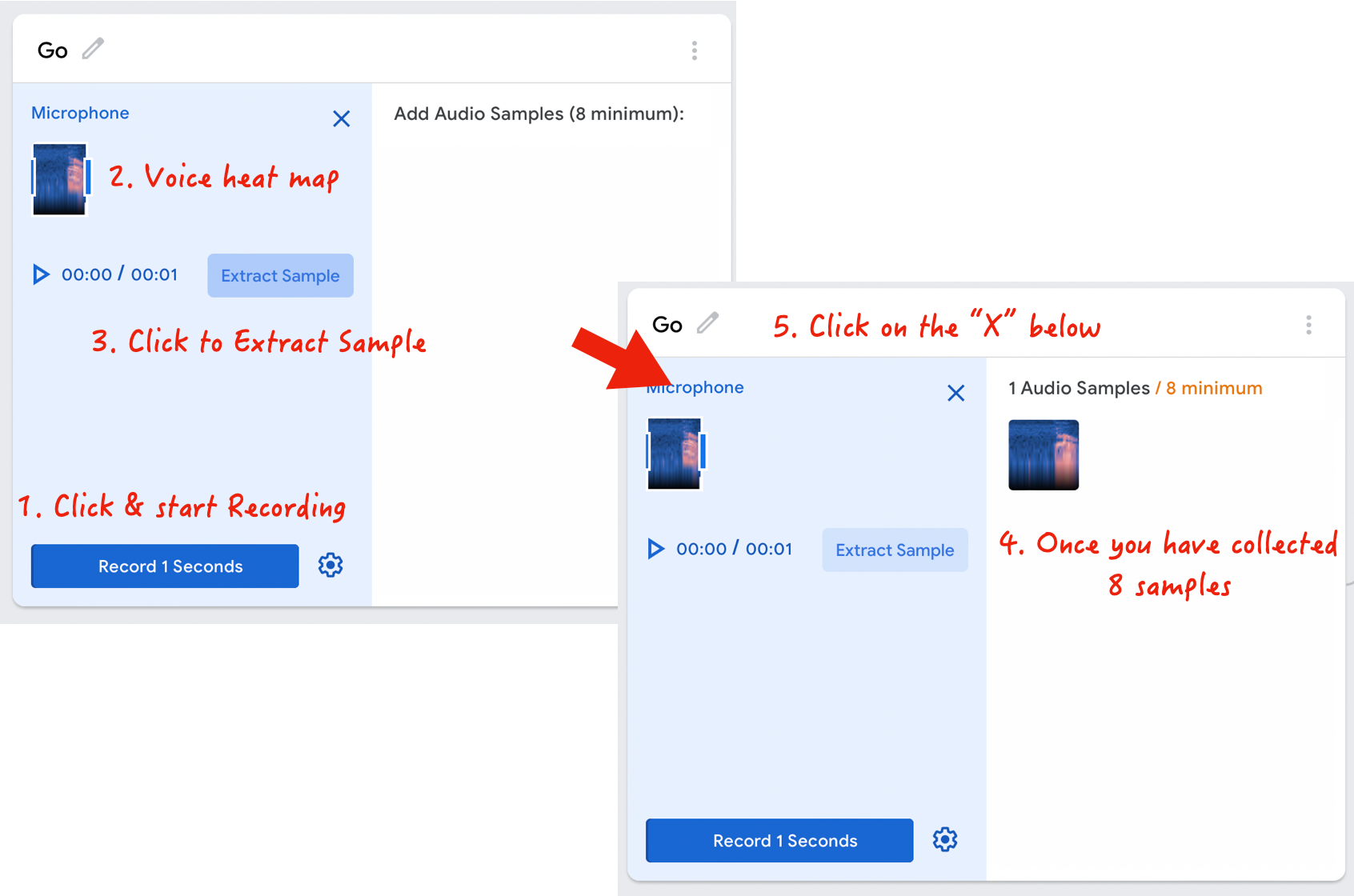
Each sampling class with take multiple 1s sound clips for training. Record a minimum of 8 samples, but I would highly recommend giving Teachable Machine more data for training.
Click on "Record 1 Seconds" to begin capturing audio from your laptop's microphone. You can observe the spectrograms heat map (the blueish graphs that visualize the sound) as you are making the recording.
Click on "Extract Sample" every time you are done with a 1s recording; once you have collected at least 8 samples (of you making the same sound), you can click on the "x" then proceed with the other recognition classes we need.
After we have collected the training data for all recognition classes, we will use Teachable Machine to train for a sound recognition training model. Hit the "Train Model" button to the right of the classes.
Once training is completed, test the model on the same page, create the sound/voice used during training & verify the A.I. inference results is working. When you are not making any sound, it the preview result should stay as "Background noise".